THE VILLAGERS OF COLLINGHAM AND LINTON WHO SERVED IN WORLD WAR TWO
COLLINGHAMANDDISTRICTWARARCHIVE.INFO
 CONTACT
CONTACT
Medals awarded
We do not have the medals of any of the men named on this site. The medal ribbons shown on the individual record pages are an indication of the medals awarded that we have been able to trace during our researches. It is possible that the men named were entitled to wear other medals awarded for conflicts. Since individual's medal entitlements have not yet been released to the public there are no full lists of medal entitlements that we can consult. We apologise if we have made any errors in medal entitlement and we will correct them as soon as we are informed.
This is not a complete list of British Medals, our list includes those medals awarded to men and women of Collingham and Linton who served in the 20th Century.
The list below will explain the award criteria for each of the medals
Orders of Chivarly
 Knight Commander of the Most Honourable Order of the Bath (KCB).
Knight Commander of the Most Honourable Order of the Bath (KCB).
 Companion of the Most Honourable Order of the Bath (CB).
Companion of the Most Honourable Order of the Bath (CB).
 Companion of the Most Honourable Order of St.Michael and St. George (CMG).
Companion of the Most Honourable Order of St.Michael and St. George (CMG).
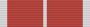 Commander of the Most Honourable Order of the British Empire (CBE).
Commander of the Most Honourable Order of the British Empire (CBE).
 Officer of the Most Honourable Order of the British Empire (OBE).
Officer of the Most Honourable Order of the British Empire (OBE).
 Member of the Most Honourable Order of the British Empire (MBE).
Member of the Most Honourable Order of the British Empire (MBE).
Gallantry Medals
 The Distinguished Service Order (DSO). Awarded for an act of meritorious or distinguished service in
wartime and usually when under fire or in the presence of the enemy.
The Distinguished Service Order (DSO). Awarded for an act of meritorious or distinguished service in
wartime and usually when under fire or in the presence of the enemy.
 The Military Cross (MC). Awarded for gallantry during active operations in the presence of the enemy.
The Military Cross (MC). Awarded for gallantry during active operations in the presence of the enemy.
 The Military Cross (MC) and Bar. Second awards of the MC are marked as MC and Bar.
The Military Cross (MC) and Bar. Second awards of the MC are marked as MC and Bar.
 The Military Medal. The Military Medal (MM) was a military decoration awarded to personnel of the British Army and other arms of the armed forces, and to personnel of other Commonwealth countries, below commissioned rank, for bravery in battle on land. The award was established in 1916, with retrospective application to 1914, and was awarded to other ranks for "acts of gallantry and devotion to duty under fire". The award was discontinued in 1993 when it was replaced by the Military Cross.
The Military Medal. The Military Medal (MM) was a military decoration awarded to personnel of the British Army and other arms of the armed forces, and to personnel of other Commonwealth countries, below commissioned rank, for bravery in battle on land. The award was established in 1916, with retrospective application to 1914, and was awarded to other ranks for "acts of gallantry and devotion to duty under fire". The award was discontinued in 1993 when it was replaced by the Military Cross.
 The Distinguished Flying Cross. The Distinguished Flying Cross (DFC) is the third-level military decoration awarded to officers, and since 1993 to other ranks, of
the United Kingdom's Royal Air Force and other services, and formerly to officers of other Commonwealth countries, for "an act or acts of valour, courage
or devotion to duty whilst flying in active operations against the enemy".
The Distinguished Flying Cross. The Distinguished Flying Cross (DFC) is the third-level military decoration awarded to officers, and since 1993 to other ranks, of
the United Kingdom's Royal Air Force and other services, and formerly to officers of other Commonwealth countries, for "an act or acts of valour, courage
or devotion to duty whilst flying in active operations against the enemy".
Long Service and Good Conduct Medals
 The General Service Medal. This medal was instituted to recognise service in minor Army operations where
no separate medal was intended.
The General Service Medal. This medal was instituted to recognise service in minor Army operations where
no separate medal was intended.


 The Meritorious Service Medal. This is awarded for distinguished service or for gallantry principally by
non-commissioned officers of all British armed forces. There are three variations of ribbon for this award: Pre-1916 - crimson; 1916-1917 - crimson with
white edges; 1917- - crimson with white edges and a white central stripe.
The Meritorious Service Medal. This is awarded for distinguished service or for gallantry principally by
non-commissioned officers of all British armed forces. There are three variations of ribbon for this award: Pre-1916 - crimson; 1916-1917 - crimson with
white edges; 1917- - crimson with white edges and a white central stripe.
Pre-First World War Medals
Some servicemen who fought in the Great War had also seen service in the Boer Wars and had been awarded medals.
 The Queen's South Africa Medal
This medal was instituted by Queen Victoria in 1900, for award to military personnel and civilian officials who served in South Africa during the Second Boer War
from 11 October 1899 to 31 May 1902.
The Queen's South Africa Medal
This medal was instituted by Queen Victoria in 1900, for award to military personnel and civilian officials who served in South Africa during the Second Boer War
from 11 October 1899 to 31 May 1902.
 The King's South Africa Medal.
This was a British campaign medal awarded to all British and Colonial military personnel who served in the Second Boer War in South Africa, and who
had served in the theatre of war between 1 January 1902 and 31 May 1902 and completed 18 months service in the conflict, not necessarily continuous,
prior to 1 June 1902. When awarded this medal was always paired with the Queen's South Africa Medal.
The King's South Africa Medal.
This was a British campaign medal awarded to all British and Colonial military personnel who served in the Second Boer War in South Africa, and who
had served in the theatre of war between 1 January 1902 and 31 May 1902 and completed 18 months service in the conflict, not necessarily continuous,
prior to 1 June 1902. When awarded this medal was always paired with the Queen's South Africa Medal.
 The Transport Medal.
The Transport Medal is a British campaign medal sanctioned on 8 November 1903, awarded by the Lord Commissioners of the Admiralty. It was awarded to masters and
officers of merchant ships employed by the Transport Service to move troops to either South Africa during the South African War or to China during the Boxer Rebellion.
The Transport Medal.
The Transport Medal is a British campaign medal sanctioned on 8 November 1903, awarded by the Lord Commissioners of the Admiralty. It was awarded to masters and
officers of merchant ships employed by the Transport Service to move troops to either South Africa during the South African War or to China during the Boxer Rebellion.
First World War Campaign Medals
Some world war two soldiers had served in The Great War and were awarded campaign medals for that conflict.
 The 1914 Star. This medal was awarded to all officers, non-commissioned officers and men of the British
and Indian Forces, including civilian nursing sisters, nurses and other employed with military hospitals, who actually served in
France or Belgium, on the establishment of a unit of the British Expeditionary Forces, between 5 August 1914 and midnight on the 22/23rd
November 1914. It could not be awarded on its own and was always accompanied by the British War Medal and the Victory Medal.
The 1914 Star. This medal was awarded to all officers, non-commissioned officers and men of the British
and Indian Forces, including civilian nursing sisters, nurses and other employed with military hospitals, who actually served in
France or Belgium, on the establishment of a unit of the British Expeditionary Forces, between 5 August 1914 and midnight on the 22/23rd
November 1914. It could not be awarded on its own and was always accompanied by the British War Medal and the Victory Medal.
 The 1914-15 Star. To qualify for this medal a soldier had to serve in a theatre of war between 5 August 1914
and 31 December 1915. However if the soldier had already qualified for the 1914 Star he would not be awarded the 1914-15 Star.
The 1914-15 Star. To qualify for this medal a soldier had to serve in a theatre of war between 5 August 1914
and 31 December 1915. However if the soldier had already qualified for the 1914 Star he would not be awarded the 1914-15 Star.
 The British War Medal. This medal had complex award criteria but basically to be eligible the serviceman
or women had to enter theatre of war or serve overseas between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918. This medal could be the sole medal
entitlement and this is often the case for soldiers garrisoning India.
The British War Medal. This medal had complex award criteria but basically to be eligible the serviceman
or women had to enter theatre of war or serve overseas between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918. This medal could be the sole medal
entitlement and this is often the case for soldiers garrisoning India.
 The Victory Medal. This medal was awarded to all servicemen and women who served in a theatre of war
between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918 and automatically qualified its recipient for the British War Medal. The Victory Medal was never awarded
on its own.
The Victory Medal. This medal was awarded to all servicemen and women who served in a theatre of war
between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918 and automatically qualified its recipient for the British War Medal. The Victory Medal was never awarded
on its own.
 The Victory Medal with Oak leaves signifying Mentioned in Dispatches. If a man was mentioned in dispatches
he would wear a Victory Medal with Oak Leaves.
The Victory Medal with Oak leaves signifying Mentioned in Dispatches. If a man was mentioned in dispatches
he would wear a Victory Medal with Oak Leaves.
 The Territorial Force War Medal. This medal was awarded to personnel of the Territorial Force and
Territorial Force Nursing Services who volunteered for service overseas on or before 30 September 1914 if they had been serving with
the force on 4 August 1914 or had completed 4 years of service with the force before 4 August 1914 and rejoined the force on or before 30 September 1914. In addition,
they had to agree to serve outside the UK, or have served outside the UK between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918. Holders of the
1914 Star or the 1914-15 Star were not eligible for this medal.
The Territorial Force War Medal. This medal was awarded to personnel of the Territorial Force and
Territorial Force Nursing Services who volunteered for service overseas on or before 30 September 1914 if they had been serving with
the force on 4 August 1914 or had completed 4 years of service with the force before 4 August 1914 and rejoined the force on or before 30 September 1914. In addition,
they had to agree to serve outside the UK, or have served outside the UK between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918. Holders of the
1914 Star or the 1914-15 Star were not eligible for this medal.
 The Silver War Badge. The badge was initially issued to officers and men who were discharged or retired
from the military forces as a result of sickness or injury caused by the war service. After 1918 it could also be awarded to civilians working with the Royal
Army Medical Corps.
The Silver War Badge. The badge was initially issued to officers and men who were discharged or retired
from the military forces as a result of sickness or injury caused by the war service. After 1918 it could also be awarded to civilians working with the Royal
Army Medical Corps.
Inter War Campaign Medals
Some soldiers served between the wars and were awarded campaign medals for those conflicts.
 The India General Service Medal (1908-1935).
The 1909 IGSM was awarded for various minor military campaigns in India from 1908 to 1935. Each campaign was represented by a clasp on the ribbon; 12 were sanctioned.
The India General Service Medal (1908-1935).
The 1909 IGSM was awarded for various minor military campaigns in India from 1908 to 1935. Each campaign was represented by a clasp on the ribbon; 12 were sanctioned.
World War Two Campaign Medals
Some world war one soldiers served in The Second World War and were awarded campaign medals for that conflict.
 The 1939-45 Star.
The 1939–1945 Star was awarded for operational service between 3 September 1939 and 2 September 1945, the duration of the Second World War. Two clasps were instituted
to be worn on the medal ribbon, along with rosettes to be worn on the ribbon bar of the medal to denote the award of a clasp.
The 1939-45 Star.
The 1939–1945 Star was awarded for operational service between 3 September 1939 and 2 September 1945, the duration of the Second World War. Two clasps were instituted
to be worn on the medal ribbon, along with rosettes to be worn on the ribbon bar of the medal to denote the award of a clasp.
 The 1939-45 Star with Battle of Britain Clasp.
Aircrew serving in Fighter Command who flew at least one operational sortie during the Battle of Britain, specifically
between July 10 and October 31, 1940 were also awarded the Battle of Britain Clasp.
The 1939-45 Star with Battle of Britain Clasp.
Aircrew serving in Fighter Command who flew at least one operational sortie during the Battle of Britain, specifically
between July 10 and October 31, 1940 were also awarded the Battle of Britain Clasp.
 The 1939-45 Star with Bomber Command Clasp.
Individuals who served as aircrew with a UK based Bomber Command unit between September 3, 1939, and May 8, 1945, and who flew
at least one operational sortie were also awarded the Bomber Command Clasp.
The 1939-45 Star with Bomber Command Clasp.
Individuals who served as aircrew with a UK based Bomber Command unit between September 3, 1939, and May 8, 1945, and who flew
at least one operational sortie were also awarded the Bomber Command Clasp.
 The 1939-45 War Medal. Awarded to subjects of the British Commonwealth who had served full-time
in the Armed Forces or the Merchant Navy for at least 28 days between 3 September 1939 and 2 September 1945.
The 1939-45 War Medal. Awarded to subjects of the British Commonwealth who had served full-time
in the Armed Forces or the Merchant Navy for at least 28 days between 3 September 1939 and 2 September 1945.
 The 1939-45 War Medal with Oak leaves signifying Mentioned in Dispatches. If a man was mentioned in dispatches
he would wear a 1939-1945 War Medal with Oak Leaves Emblem.
The 1939-45 War Medal with Oak leaves signifying Mentioned in Dispatches. If a man was mentioned in dispatches
he would wear a 1939-1945 War Medal with Oak Leaves Emblem.
 The Defence Medal.
The Defence Medal was awarded for non-operational service in the Armed Forces, the Home Guard, the Civil Defence Service
and other approved civilian services during the period from 3 September 1939 to 2 September 1945 inclusive.
The Defence Medal.
The Defence Medal was awarded for non-operational service in the Armed Forces, the Home Guard, the Civil Defence Service
and other approved civilian services during the period from 3 September 1939 to 2 September 1945 inclusive.
 The Atlantic Star. This medal was awarded to subjects of the British Commonwealth who took part
in the Battle of the Atlantic during the Second World War.
The Atlantic Star. This medal was awarded to subjects of the British Commonwealth who took part
in the Battle of the Atlantic during the Second World War.
 The Atlantic Star with Clasp.
Individuals who became eligible for either of the Air Crew Europe or France and Germany Star after the award of the Atlantic Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s).
The Atlantic Star with Clasp.
Individuals who became eligible for either of the Air Crew Europe or France and Germany Star after the award of the Atlantic Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s).
 The Africa Star.
The Africa Star was awarded for a minimum of one day's service in an operational area of North Africa between 10 June 1940 and 12 May 1943.
The Africa Star.
The Africa Star was awarded for a minimum of one day's service in an operational area of North Africa between 10 June 1940 and 12 May 1943.
 The Africa Star with First Army Clasp. If the individual
served with the First Army between 8 November 1942 and 12 May 1943 inclusive, The 1st Army Clasp was also awarded.
The Africa Star with First Army Clasp. If the individual
served with the First Army between 8 November 1942 and 12 May 1943 inclusive, The 1st Army Clasp was also awarded.
 The Africa Star with Eighth Army Clasp.
If the individual
served with the Eighth Army between 23 October 1942 and 12 May 1943 inclusive, The 8th Army Clasp was also awarded.
The Africa Star with Eighth Army Clasp.
If the individual
served with the Eighth Army between 23 October 1942 and 12 May 1943 inclusive, The 8th Army Clasp was also awarded.
 The Africa Star with Rosette. The North Africa 1942–43 Clasp was awarded for
service with the 18th Army Group Headquarters between 15 February 1942 and 12 February 1943 inclusive, for Navy and Merchant Navy personnel
in shore service, or for Air Force service in specified areas from 23 October 1942 to 12 May 1943 inclusive.
The Africa Star with Rosette. The North Africa 1942–43 Clasp was awarded for
service with the 18th Army Group Headquarters between 15 February 1942 and 12 February 1943 inclusive, for Navy and Merchant Navy personnel
in shore service, or for Air Force service in specified areas from 23 October 1942 to 12 May 1943 inclusive.
 The Arctic Star.
The Arctic Star was awarded to British Commonwealth forces who served on the Arctic Convoys north of the Arctic Circle, during the Second World War.
The Arctic Star.
The Arctic Star was awarded to British Commonwealth forces who served on the Arctic Convoys north of the Arctic Circle, during the Second World War.
 The Air Crew Europe Star.
The Air Crew Europe Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth air
crews who participated in operational flights over Europe from bases in the United Kingdom during the Second World War.
The Air Crew Europe Star.
The Air Crew Europe Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth air
crews who participated in operational flights over Europe from bases in the United Kingdom during the Second World War.
 The Air Crew Europe Star with Rosette.
Individuals who became eligible for either of the Atlantic or France and Germany Star after the award of the Air Crew Europe Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s).
The Air Crew Europe Star with Rosette.
Individuals who became eligible for either of the Atlantic or France and Germany Star after the award of the Air Crew Europe Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s).
 The Pacific Star.
The Pacific Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth forces who served in the Pacific Campaign from 1941 to 1945, during the Second World War.
The Pacific Star.
The Pacific Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth forces who served in the Pacific Campaign from 1941 to 1945, during the Second World War.
 The Pacific Star with Rosette.
Individuals who became eligible for the Burma Star after the award of the Pacific Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s).
The Pacific Star with Rosette.
Individuals who became eligible for the Burma Star after the award of the Pacific Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s).
 The Burma Star.
The Burma Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth forces who served in the Burma Campaign from 1941 to 1945.
The Burma Star.
The Burma Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth forces who served in the Burma Campaign from 1941 to 1945.
 The Burma Star with Rosette
Individuals who became eligible for the Pacific Star after the award of the Burma Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s)..
The Burma Star with Rosette
Individuals who became eligible for the Pacific Star after the award of the Burma Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s)..
 The Italy Star.
The Italy Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth forces who served in the Italian Campaign from 1943 to 1945.
The Italy Star.
The Italy Star was awarded to British and Commonwealth forces who served in the Italian Campaign from 1943 to 1945.
 The France and Germany Star.
The France and Germany Star was awarded to British Commonwealth forces who served in France, Belgium, Luxembourg, the Netherlands or Germany
and adjacent sea areas between 6 June 1944 and 8 May 1945.
The France and Germany Star.
The France and Germany Star was awarded to British Commonwealth forces who served in France, Belgium, Luxembourg, the Netherlands or Germany
and adjacent sea areas between 6 June 1944 and 8 May 1945.
 The France and Germany Star with Rosette
Individuals who became eligible for the Atlantic Star after the award of the France and Germany Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s)..
The France and Germany Star with Rosette
Individuals who became eligible for the Atlantic Star after the award of the France and Germany Star
were awarded a clasp to signify the later award(s)..
 The Australian Service Medal 1939-45 War Medal recognises service in Australia's armed forces,
Mercantile Marine and Volunteer Defence Corps during World War II. Initially, the qualifying period was at least 18 months full-time service at home
or overseas, or at least three years part-time service, between 3 September 1939 and 2 September 1945. There was no minimum qualifying
period for those killed, wounded or disabled due to service. On 16 August 1996, the qualifying period was reduced to 30 days
for full-time service and 90 days for part-time service. Australian Forces also qualified for the campaign stars and medals authorised
for British and Commonwealth Forces, with the Australia Service Medal worn immediately after the War Medal 1939–1945.
The Australian Service Medal 1939-45 War Medal recognises service in Australia's armed forces,
Mercantile Marine and Volunteer Defence Corps during World War II. Initially, the qualifying period was at least 18 months full-time service at home
or overseas, or at least three years part-time service, between 3 September 1939 and 2 September 1945. There was no minimum qualifying
period for those killed, wounded or disabled due to service. On 16 August 1996, the qualifying period was reduced to 30 days
for full-time service and 90 days for part-time service. Australian Forces also qualified for the campaign stars and medals authorised
for British and Commonwealth Forces, with the Australia Service Medal worn immediately after the War Medal 1939–1945.
Only a maximum of 6 campaign stars for world war 2 can be awarded with five of the ten clasps awarded denoting service that would have qualified for a second star.
The maximum of six possible stars are the following:
The 1939–1945 Star with, when awarded, either the Battle of Britain or the Bomber Command clasp.
Only one of the Atlantic Star, Air Crew Europe Star or France and Germany Star. Those earning more than one received the first qualified for, with the second
denoted by the appropriate ribbon clasp.
The Arctic Star.
The Africa Star with, if awarded, the first to be earned of clasps for North Africa 1942–43, 8th Army or 1st Army.
Either the Pacific Star or Burma Star. Those earning both received the first qualified for, with the appropriate clasp to represent the second.
The Italy Star.
All recipients of World War 2 campaign stars also received the War Medal.
Coronation, Long Service and other medals
 The Efficiency Medal or The Territorial Efficiency Medal.
The Efficiency Medal was instituted in 1930 for award to part-time warrant officers, non-commissioned officers and men after twelve years of efficient service on the active list of the Militia or the Territorial Army of the United Kingdom, or of the other Auxiliary Military Forces throughout the British Empire. It superceeded the
Territorial Efficiency Medal.
The Efficiency Medal or The Territorial Efficiency Medal.
The Efficiency Medal was instituted in 1930 for award to part-time warrant officers, non-commissioned officers and men after twelve years of efficient service on the active list of the Militia or the Territorial Army of the United Kingdom, or of the other Auxiliary Military Forces throughout the British Empire. It superceeded the
Territorial Efficiency Medal.
 Queen Victoria Diamond Jubilee Medal 1897.
The medal was awarded to those involved in the official celebrations of Queen Victoria's diamond jubilee, including members of the Royal Family, Royal
Household and government officials, as well as Envoys, Foreign Ambassadors and Colonial Prime Ministers. Military recipients included selected officers,
sailors and soldiers of the Royal Navy and Army, and the Indian and colonial contingents, that participated in jubilee activities, including the London
procession in which the Queen took part.
Queen Victoria Diamond Jubilee Medal 1897.
The medal was awarded to those involved in the official celebrations of Queen Victoria's diamond jubilee, including members of the Royal Family, Royal
Household and government officials, as well as Envoys, Foreign Ambassadors and Colonial Prime Ministers. Military recipients included selected officers,
sailors and soldiers of the Royal Navy and Army, and the Indian and colonial contingents, that participated in jubilee activities, including the London
procession in which the Queen took part.
 1937 Coronation Medal.
This medal was awarded as a personal souvenir of King George VI's coronation. It was awarded to the Royal Family and selected officers of state, officials and servants
of the Royal Household, ministers, government officials, mayors, public servants, local government officials, members of the navy, army, air force and police in
Britain, her colonies and Dominions.
1937 Coronation Medal.
This medal was awarded as a personal souvenir of King George VI's coronation. It was awarded to the Royal Family and selected officers of state, officials and servants
of the Royal Household, ministers, government officials, mayors, public servants, local government officials, members of the navy, army, air force and police in
Britain, her colonies and Dominions.
 1953 Coronation Medal.
This medal was awarded as a personal souvenir of Queen Elizabeth II's coronation from the Queen to members of the Royal Family and selected officers of state, members of the
Royal Household, government officials, mayors, public servants, local government officials, members of the navy, army, air force
and police in Britain, her colonies and Dominions. It was also awarded to members of the Mount Everest expedition, two of whom reached
the summit four days before the coronation.
1953 Coronation Medal.
This medal was awarded as a personal souvenir of Queen Elizabeth II's coronation from the Queen to members of the Royal Family and selected officers of state, members of the
Royal Household, government officials, mayors, public servants, local government officials, members of the navy, army, air force
and police in Britain, her colonies and Dominions. It was also awarded to members of the Mount Everest expedition, two of whom reached
the summit four days before the coronation.
 Meritorious Service Medal.
is a British medal awarded to sergeants and warrant officers of the British armed forces for long and meritorious service. From 1916 to 1928, eligibility was
extended to cover both valuable services by selected other ranks irrespective of length of service, and for gallantry not in the face of the enemy.
Meritorious Service Medal.
is a British medal awarded to sergeants and warrant officers of the British armed forces for long and meritorious service. From 1916 to 1928, eligibility was
extended to cover both valuable services by selected other ranks irrespective of length of service, and for gallantry not in the face of the enemy.
 Long Service and Good Conduct Medal.
The Medal for Long Service and Good Conduct (Military) is a medal awarded to regular members of the armed forces. It was instituted by King George V in 1930 and replaced
the Army Long Service and Good Conduct Medal as well as the Permanent Forces of the Empire Beyond the Seas Medal. The medal was originally awarded to Regular Army
warrant officers, non-commissioned officers and men of the UK Armed Forces. It also had a number of territorial versions for the Permanent Forces of the British Dominions.
Long Service and Good Conduct Medal.
The Medal for Long Service and Good Conduct (Military) is a medal awarded to regular members of the armed forces. It was instituted by King George V in 1930 and replaced
the Army Long Service and Good Conduct Medal as well as the Permanent Forces of the Empire Beyond the Seas Medal. The medal was originally awarded to Regular Army
warrant officers, non-commissioned officers and men of the UK Armed Forces. It also had a number of territorial versions for the Permanent Forces of the British Dominions.
Royal Naval Reserve Decoration.
The Decoration for Officers of the Royal Naval Reserve, commonly known as the Reserve Decoration (RD) was a medal awarded to officers with at least fifteen years
service in the Royal Naval Reserve (RNR) of the United Kingdom. The fifteen years' service could not count service as a midshipman, with wartime service counting double.
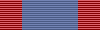 The Royal Red Cross
is a military decoration awarded in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth for exceptional services in military nursing. The award is made to a fully trained nurse of an
officially recognised nursing service, military or civilian, who has shown exceptional devotion and competence in the performance of nursing duties,
over a continuous and long period, or who has performed an exceptional act of bravery and devotion at her or his post of duty.
The Royal Red Cross
is a military decoration awarded in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth for exceptional services in military nursing. The award is made to a fully trained nurse of an
officially recognised nursing service, military or civilian, who has shown exceptional devotion and competence in the performance of nursing duties,
over a continuous and long period, or who has performed an exceptional act of bravery and devotion at her or his post of duty.